How can we avoid the warming effect of reducing polluted air?
- The increase in global warming that has been noted in recent years is partly a consequence of the reduction in pollution, because the decreasing sulphur aerosol emissions compensate for part of the greenhouse effect itself. This paradox introduces us to a new situation, we have cleaner air, but in an atmosphere that heats up faster. How can we continue to breathe clean air without increasing the climate imbalance?

Maybe you've heard it or read it in a social network, among several catastrophic headlines that line up: the rate of global warming has increased in recent years. This is a bad sign, because in addition to questioning our adaptation plans, how long does it take until too many things can be overcome?, it forces us to increase the rate of emission reductions.
Between 1970 and 2014, the warming trend was 0.18 degrees in the decade. However, temperatures since 2015 have been significantly higher, with the largest difference being the one observed in 2023 and the second highest in 2015-2016. These two moments have a common element: Phenomenon called El Niño. But before El Niño was also a time, and today we continue to live one, which is not particularly strong. It's not only that that accelerates the warming trend. This acceleration of warming is not based on all the lights, or better if it is more than one factor and its influence remains the object of specific study.
The climatologist James Hansen is one of the first to sound the alarm about warming in the 1980s. This acceleration was analyzed in the article Global warming in the pipeline, published last November with a large group. In a note on this work he has published in January, he considers the darkening of the planet as the main factor. This doesn't mean we get alarmed at nights, but the planet doesn't reflect the sun's rays in space as before, so we get more solar radiation into the Earth's surface and into the ocean. Again, in recent years, the Earth has lost its albedo. The loss of albedo in such a few years is related to a faster melting of ice from mountains and poles, but not only to the measures taken to improve air quality. By reducing air pollution, we darken the planet and warmer more. How is that possible?
Benefits and damages in sulphur aerosols
In the atmosphere there are small particles called aerosols, of a few micrometers, that remain suspended in the air. Dust or knives from deserts, sea flames, volcanic and fire dust forestales.Tambi are also sources of aerosols engines and factories, especially if "dirty" fuels are used, i.e. gas oil or sulphur-rich coal. Sulphur aerosols do not accumulate infrared rays in the atmosphere, as do greenhouse gases, but they increase terrestrial albedo, reflecting some of the rays coming from the sun. Through it, they offset some of the effects of greenhouse gases, up to a third, until 2014, when China took measures on the quality of the aire.El problem is that aerosols not only affect the heat balance of the atmosphere, but also affect the health of those who breathe the low atmosphere daily in industrial
regions. The phenomenon of smog pollution in industrialized countries has been very frequent since the 19th century. Despite the improvement in the situation over time, in the decade of 2010 it is estimated that every year in the European Union nearly 300,000 people died from air pollution, knowing that the European situation is not the worst in the world. Globally, WHO estimates that four million people
die each year from cancer related to air pollution, lung disease, or heart disease. China's worst situation at the beginning of the century was due, on the one hand, to become the "global factory", where part of the global west's pollution was relocated, and, on the other hand, to having very weak rules on air pollution, which is why it was also cheaper to produce it in China. This last factor has changed substantially since 2013, when Xi Jinping has prescribed stricter controls in heavy industries. According to meteorologist Xiao-Tong Zheng of the Chinese Ocean University, in the decade aerosol emissions have been reduced by 70% and sulphur dioxide emissions by 88%.
So what, you have to leave the pollution like before?
The Chinese proverb says that the movement of a butterfly's wings can feel at the other end of the world. In this case, a lower emission of aerosols in China has produced heat waves in the northeast Pacific. This has been demonstrated by Zhenge, published in March with its Atmosphere teleconnections from abatement of China aerosol emissions exacerbate Northeast Pacific warm blob events (atmospheric teleconexions to reduce aerosol emissions in China reinforce marine heat wave events in the north-east Pacific). In addition to opening the way to the rays of the sun, it transformed the pressures of the air, deepening into the Aleutian depression and moving south, which slowed the winds to the east and increased the temperature of the sea surface.
How many more teleconquets of this kind are there in the world? Beyond the Pacific, the new standards on global cargo fuels in 2020 have shown that warming has been reinforced by the Abrupt reduction in shipping emissions as an unadvertent geoengineering termination shock produces sustantial radiative warming from the Maryland State Goddard Space Flight Center. I'm sure this "involuntary geoengineering" has made some of them come up with ideas.
Air pollution is still dying. At the moment, the most polluted regions are South Asia and Africa, and it is no coincidence that some of the most toxic waste in the world, such as electronic waste, is sent to these regions. With regard to air quality, more and more regions of the world set standards and these trends will not return again. The injustice they suffer in Africa and Sudasia must now be resolved. It is possible to breathe cleaner air and reduce global warming. An accessible solution is to cut methane discharges, particularly from fossil fuel extraction and transport infrastructures. In order to avoid the worst, we do not go too late, but for that we do or do have to take the step.
On the night of April 28, the terraces of Barcelona’s Badal Rambla were crowded; unrefrigerated beers were served, but people seemed happy. “If the end of the world has to come, let it catch us with joy,” a neighbor told me. For more than ten hours the electricity had... [+]
Klima aldaketaren eraginez, munduko lurralde gero eta gehiago idortzen ari dira, milioika pertsonaren jarduera eta bizimoduak kolokan ezarririk. Fenomeno horren frontean dago India erdialdeko Maharashtra estatua, non klimaren berotzeari eta lehortzeari metatu zaizkien oihan... [+]
Today’s Venice is built on an archipelago of 118 islands. These islands are connected by 455 bridges. The city is based on mud rather than Lura. Millions of trees in the area were cut down from the 9th century onwards to build piles and cement the city. Years have passed and... [+]
Lurrak guri zuhaitzak eman, eta guk lurrari egurra. Egungo bizimoldea bideraezina dela ikusita, Suitzako Alderdi Berdearen gazte adarrak galdeketara deitu ditu herritarrak, “garapen” ekonomikoa planetaren mugen gainetik jarri ala ez erabakitzeko. Izan ere, mundu... [+]
Eskola inguruko natur guneak aztertu dituzte Hernaniko Lehen Hezkuntzako bost ikastetxeetako ikasleek. Helburua, bikoitza: klima larrialdiari aurre egiteko eremu horiek identifikatu eta kontserbatzea batetik, eta hezkuntzarako erabiltzea, bestetik. Eskola bakoitzak natur eremu... [+]
Agintari gutxik aitortzen dute publikoki, disimulurik eta konplexurik gabe, multinazional kutsatzaileen alde daudela. Nahiago izaten dute enpresa horien aurpegi berdea babestu, “planetaren alde” lan egiten ari direla harro azpimarratu, eta kutsadura eta marroiz... [+]
Biologian doktorea, CESIC Zientzia Ikerketen Kontseilu Nagusiko ikerlaria eta Madrilgo Rey Juan Carlos unibertsitateko irakaslea, Fernando Valladares (Mar del Plata, 1965) klima aldaketa eta ingurumen gaietan Espainiako Estatuko ahots kritiko ezagunenetako bat da. Urteak... [+]
Nola azaldu 10-12 urteko ikasleei bioaniztasunaren galerak eta klima aldaketaren ondorioek duten larritasuna, “ez dago ezer egiterik” ideia alboratu eta planetaren alde elkarrekin zer egin dezakegun gogoetatzeko? Fernando Valladares biologoak hainbat gako eman dizkie... [+]
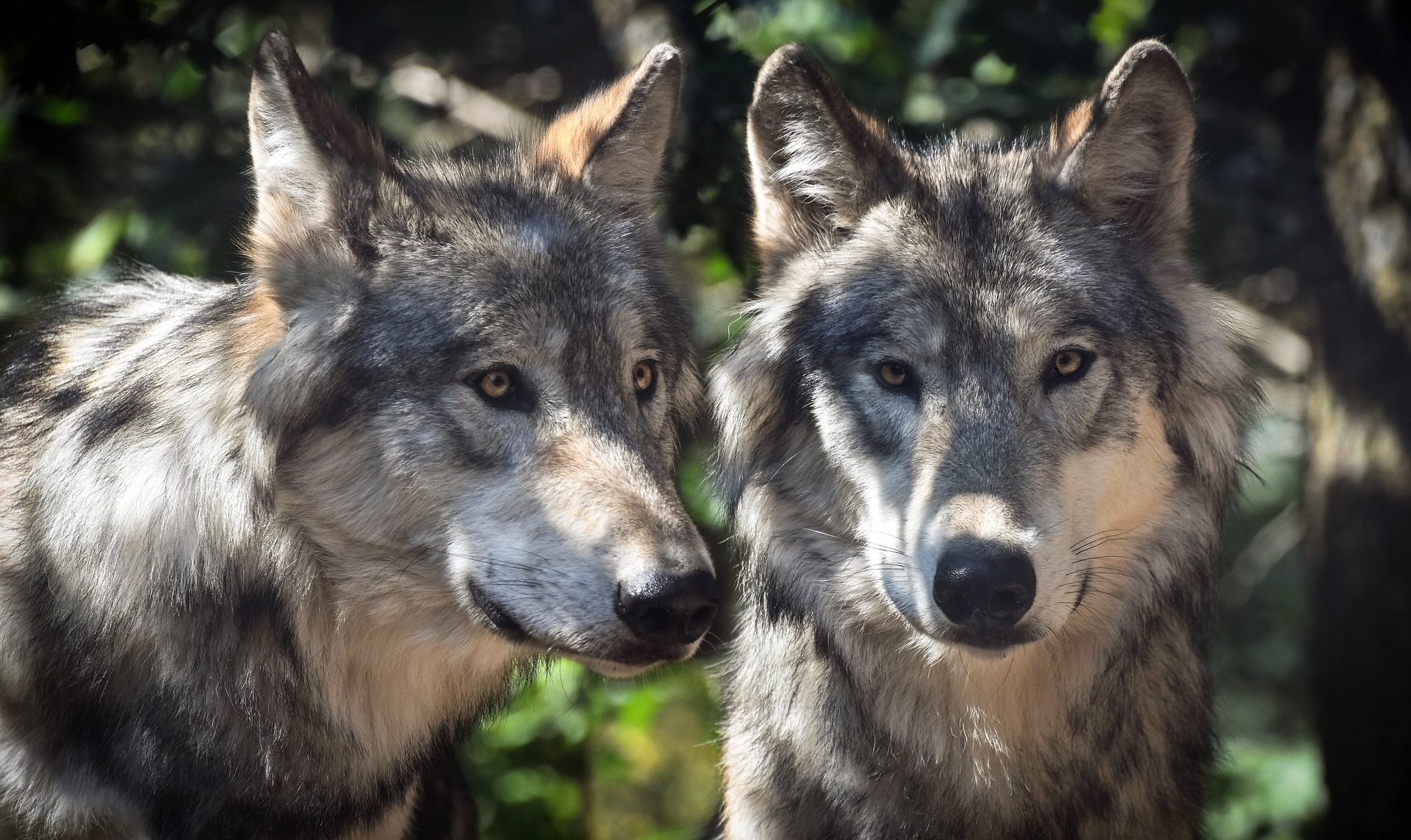
Eskoziako Lur Garaietara otsoak itzularazteak basoak bere onera ekartzen lagunduko lukeela adierazi dute Leeds unibertsitateko ikertzaileek.. Horrek, era berean, klima-larrialdiari aurre egiteko balioko lukeela baieztatu dute, basoek atmosferako karbono-dioxidoa xurgatuko... [+]