Independence of the Buddha's Hand
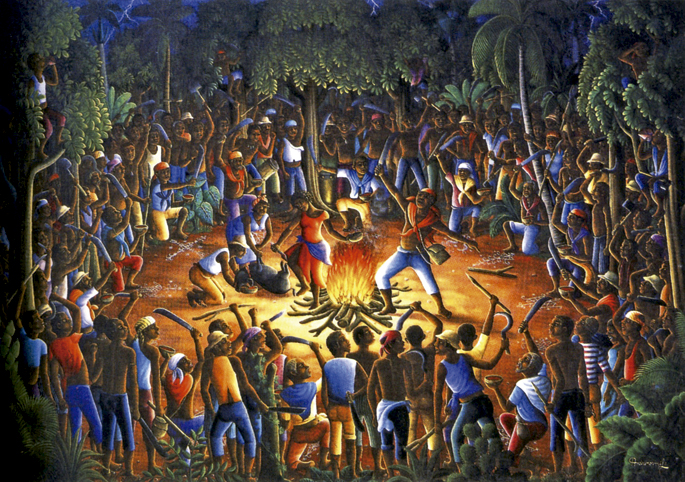

Born 14 August 1791. Several slaves, under the command of Dutty Boukman Houngan or the priest, met at a voodoo ceremony. Boukman, after naming the leaders of the movement, urged them to stand up against the French oppressors.
A week later, on the night of 21 August, the slaves of Saint-Dominguez, which was called the French colony, were raised and the Haitian Revolution began.
Although Bois-Caiman is considered the catalyst of the revolt, the lack of evidence and the few fuzzy testimonies have opened the way to varied versions. David Geggus, historian of the University of Florida, says that the caiman forest did not hold a single meeting. First, there was a ceremony of about 200 people, mainly religious. And two or three days later, a more clandestine meeting was held between Boukman and the leaders of the revolution to plan the uprising.
Several Haitian historians have questioned Bois-Caiman. Specifically, Léon-François Hoffmann stated in 1991 that Antoine Dalmas, a French plantation physician, was the inventor of history to despise slaves and their beliefs.
The myth or reality, according to Swedish researcher Markel Thylefors, “the episode of Bois-Caiman is an important part of the national identity of the Haitians, as it is linked to Haiti’s own generation”.
Haiti was the most important slave revolt since the time of Spartacus. Unlike the uprising in Ancient Rome, slaves were won in Haiti. The revolution changed the institution of slavery, provoked a review of relations between races and rocked European colonialism. The conversion of the balance of power in the Atlantic was also inevitable. At home, the slaves were liberated, fought to maintain freedom and, in 1804, founded the sovereign state of Haiti.
The nearsighted view of the West has limited the introduction of needles into the wrists to harm a bouquet. For those Caribbean slaves, it was much more. In the words of David Geggus, “the Buddha of Bois-Caiman became a unifying and revolutionary force.”
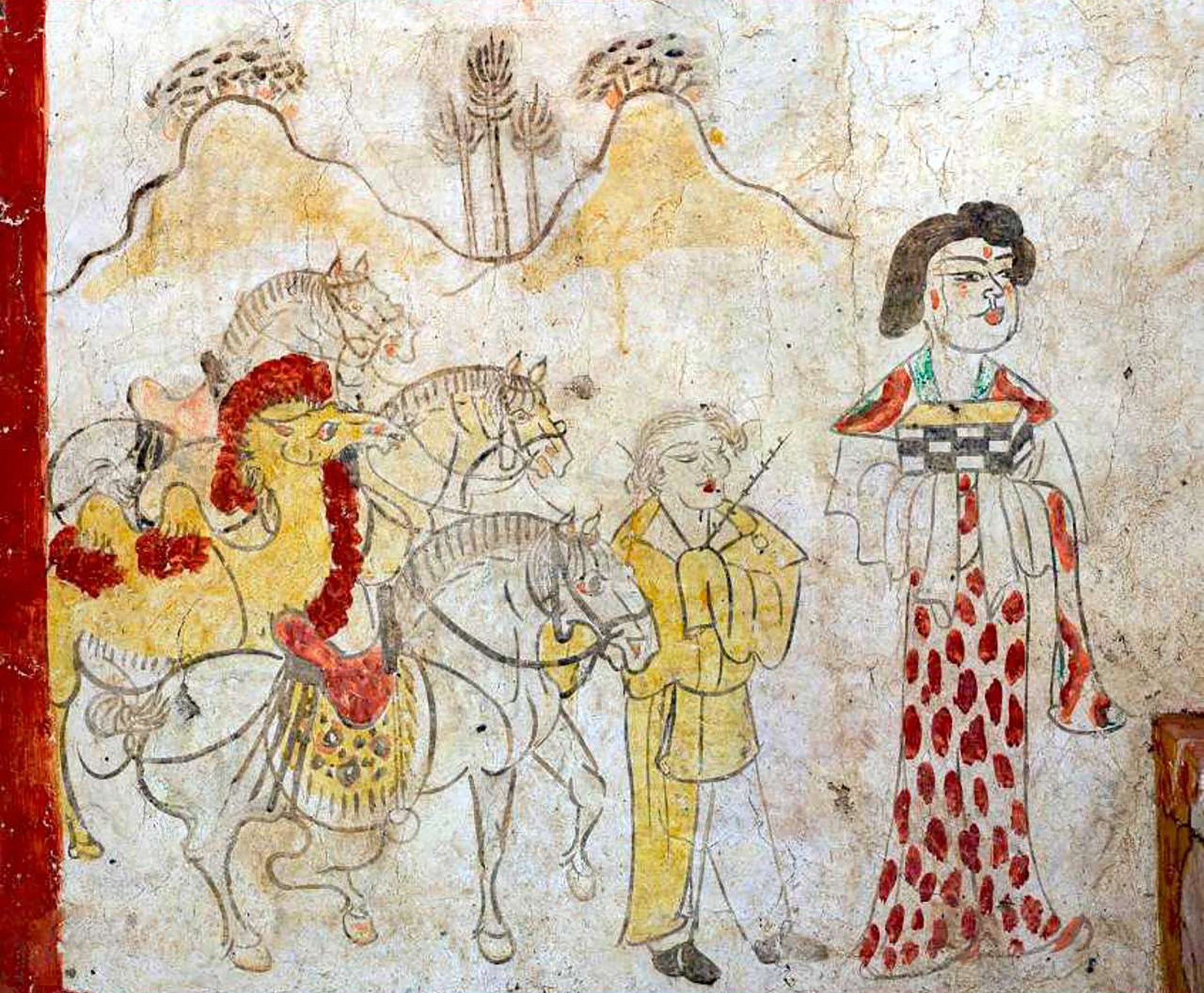
In the Chinese province of Shanxi, in a tomb of the Tang dynasty, paintings depicting scenes from the daily lives of the dead are found. In one of these scenes a blonde man appears. Looking at the color of the hair and the facial expression, archaeologists who have studied the... [+]
Carthage, from B.C. Around the 814. The Phoenicians founded a colony and the dominant civilization in the eastern Mediterranean spread to the west. Two and a half centuries later, with the decline of the Phoenician metropolis of Tyre, Carthage became independent and its... [+]
Salvador Puig Antich frankismoaren kontrako militantea izan zen. Askapen Mugimendu Iberikoko kidea, 1973ko irailaren 25ean atxilotu zuten. Gerra-kontseilua egin zioten, eta garrotez exekutatu zuten handik sei hilabetera, 1974ko martxoaren 2an. Aurtengo otsailean baliogabetu du... [+]
Rudolf Botha hizkuntzalari hegoafrikarrak hipotesi bat bota berri du Homo erectus-i buruz: espezieak ahozko komunikazio moduren bat garatu zuen duela milioi bat urte baino gehiago. Homo sapiens-a da, dakigunez, hitz egiteko gai den espezie bakarra eta, beraz, hortik... [+]
Böblingen, Holy Roman Empire, 12 May 1525. Georg Truchsess von Waldburg overthrew the Württemberg insurgent peasants. Three days later, on 15 May, Philip of Hesse and the Duke of Saxony joined forces to crush the Thuringian rebels in Frankenhausen, killing some 5,000 peasants... [+]
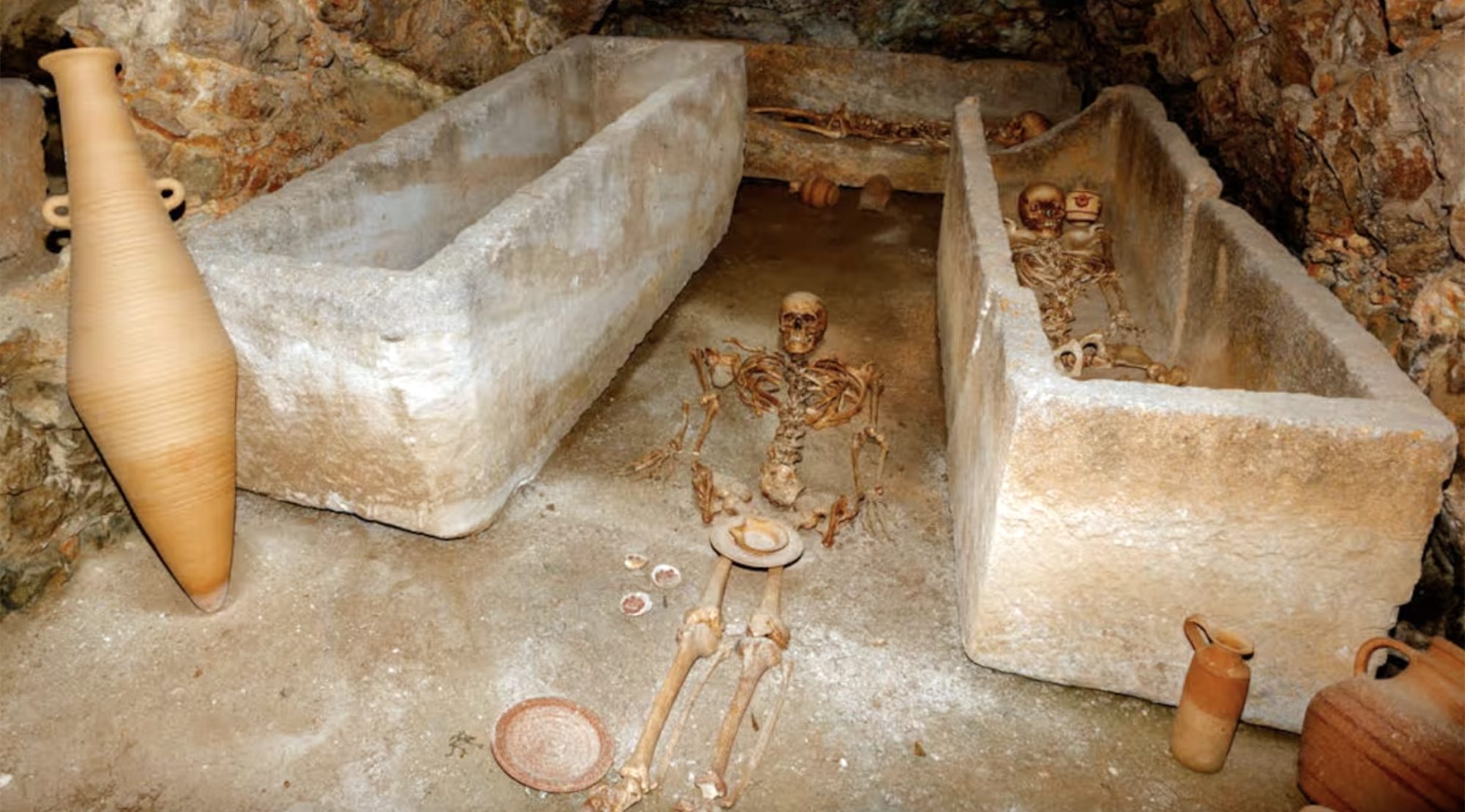
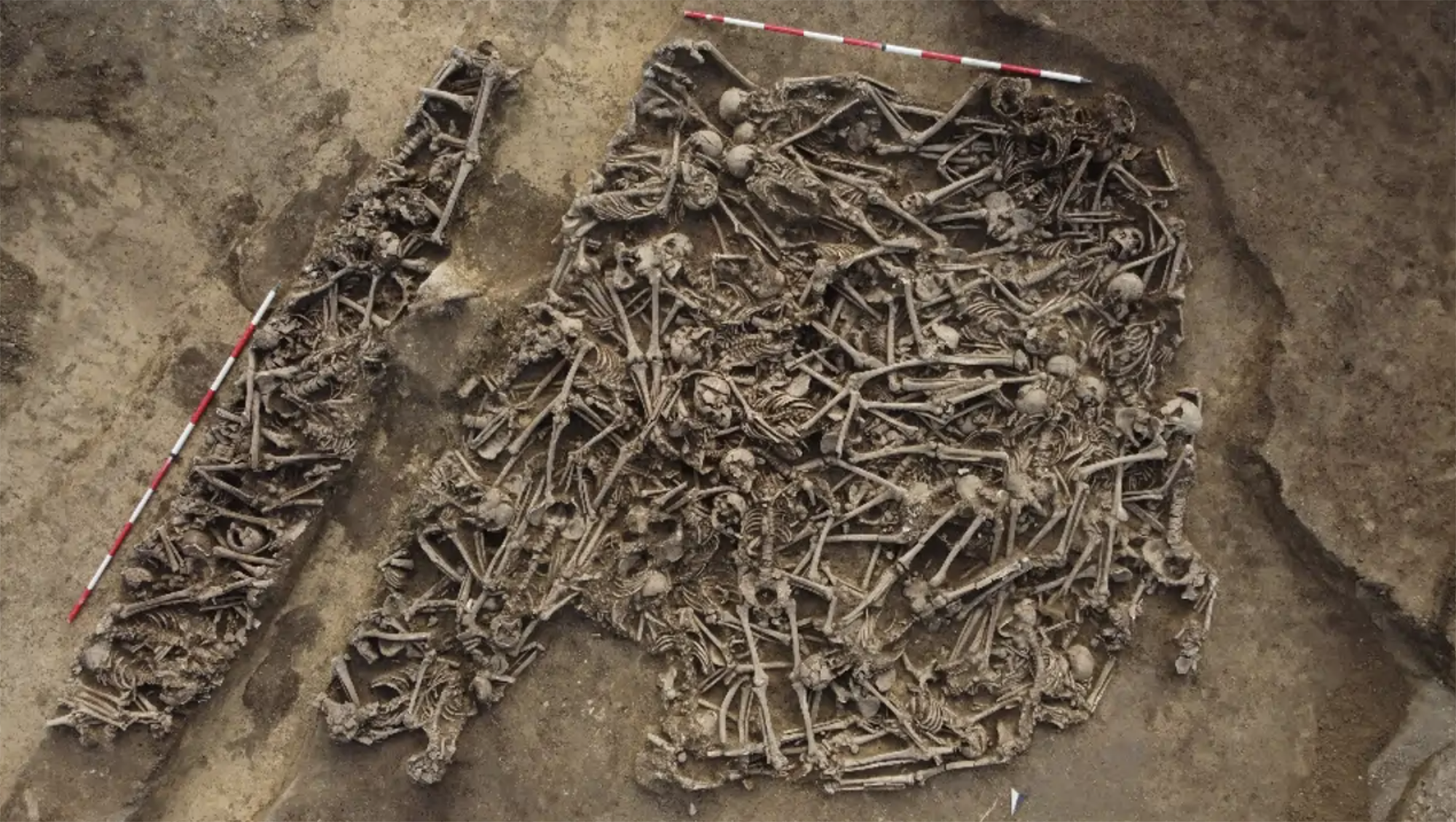
During the renovation of a sports field in the Simmering district of Vienna, a mass grave with 150 bodies was discovered in October 2024. They conclude that they were Roman legionnaires and A.D. They died around 100 years ago. Or rather, they were killed.
The bodies were buried... [+]
Washington, D.C., June 17, 1930. The U.S. Congress passed the Tariff Act. It is also known as the Smoot-Hawley Act because it was promoted by Senator Reed Smoot and Representative Willis Hawley.
The law raised import tax limits for about 900 products by 40% to 60% in order to... [+]